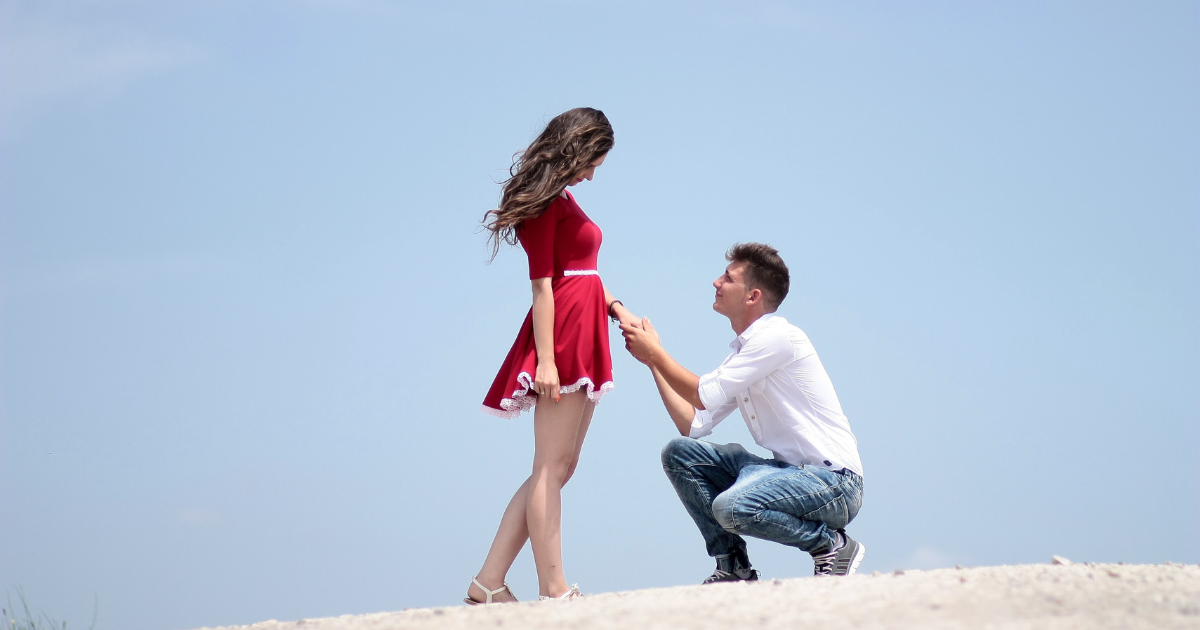
Love is a complex and multifaceted emotion that manifests in various forms across different cultures and individuals. While love is a universal experience, its expression and meaning can vary widely depending on personal experiences, cultural backgrounds, and individual perspectives. In this article, we will explore the different types of love, how they are experienced by people, and what they mean to different individuals. By delving into real-world examples, engaging anecdotes, and thought-provoking questions, we aim to offer a comprehensive understanding of this profound emotion.
Eros: Passionate and romantic love characterized by intense attraction and desire.
Philia: Deep, affectionate friendship based on mutual respect and shared values.
Storge: Familial love marked by natural affection and unconditional support.
Agape: Selfless, unconditional love that involves giving without expecting anything in return.
Ludus: Playful and flirtatious love focused on fun and enjoyment without serious commitment.
Pragma: Practical, enduring love developed through shared goals and long-term commitment.
Mania: Obsessive and possessive love characterized by intense dependency and insecurity
1. Romantic Love: The Classic Narrative
Romantic love is often considered the quintessential form of love, characterized by deep emotional and physical attraction. It is commonly portrayed in literature, films, and media as the ideal form of love.
Example: Think of classic love stories like Romeo and Juliet or modern romances like The Notebook. These portrayals emphasize passionate connections and the idea of finding a soulmate.
Anecdote: A friend of mine met their partner in college, and their relationship started as a deep friendship that blossomed into romantic love. They often describe their connection as a blend of excitement and profound understanding, which has made their bond resilient over time.
Question: How does romantic love differ from the love you see in media versus your own experiences? Reflecting on this can help you understand the nuances of romantic love in your life.
Statistic: According to a survey by Psychology Today, 68% of people describe romantic love as a central part of their life and relationships, highlighting its significant role in many individuals’ lives.
2. Platonic Love: Deep Bonds Without Romance
Platonic love refers to deep, non-romantic affection and connection between friends. It is characterized by emotional intimacy, trust, and mutual respect without romantic or sexual elements.
Example: Consider the close friendships depicted in TV shows like Friends or Parks and Recreation. These relationships are marked by strong emotional bonds and a supportive network.
Anecdote: A colleague shared that their closest friend has been a source of unwavering support throughout challenging times. They describe their platonic love as one of the most meaningful relationships in their life, offering a sense of belonging and comfort.
Question: How do you differentiate between platonic love and romantic love in your relationships? Understanding these distinctions can help you appreciate the unique qualities of each type of love.
Statistic: Research from The Journal of Social Psychology shows that 57% of people consider their closest friendships to be as fulfilling and important as romantic relationships.
3. Familial Love: The Bonds of Kinship
Familial love encompasses the affection and attachment found within family relationships. This type of love is often marked by a sense of duty, loyalty, and shared history.
Example: Think of the love parents have for their children or the close-knit bonds between siblings. This love is characterized by both emotional support and practical caregiving.
Anecdote: A family member once shared that the love they feel for their siblings is deeply rooted in shared experiences and childhood memories. This familial bond provides a sense of stability and unconditional support.
Question: How does familial love shape your identity and sense of self? Exploring this question can reveal how family relationships impact your overall well-being.
Statistic: According to a study published in Family Relations, 74% of individuals rate their family relationships as a primary source of emotional support and happiness.
4. Self-Love: Embracing Your Own Worth
Self-love involves cultivating a positive relationship with oneself. It encompasses self-acceptance, self-compassion, and recognizing one’s own value and worth.
Example: Practices like mindfulness, affirmations, and self-care routines are often associated with self-love. For instance, someone might engage in regular self-care activities to nurture their well-being.
Anecdote: A friend of mine found that developing self-love was transformative for their personal growth. By focusing on self-compassion and setting healthy boundaries, they experienced increased confidence and a more fulfilling life.
Question: How do you practice self-love in your daily life? Reflecting on this can help you identify areas for growth and self-improvement.
Statistic: Research from Psychology Today indicates that individuals who practice self-love and self-care report higher levels of happiness and overall life satisfaction.
5. Unconditional Love: Loving Without Conditions
Unconditional love is characterized by an unwavering, non-judgmental affection that is not dependent on any conditions or circumstances. This type of love is often associated with parental love but can extend to other relationships as well.
Example: The love a parent feels for their child, regardless of the child’s actions or behavior, is often cited as an example of unconditional love. This love persists despite challenges and difficulties.
Anecdote: A colleague shared that their relationship with their pet exemplifies unconditional love. Despite their pet’s quirks and occasional misbehavior, the bond remains strong and enduring.
Question: What does unconditional love mean to you, and how does it manifest in your relationships? Understanding this can deepen your appreciation for the nature of unconditional love.
Statistic: According to a study by The Journal of Emotional Health, 65% of individuals believe that experiencing or giving unconditional love is a key factor in overall emotional well-being.
6. Compassionate Love: Empathy and Understanding
Compassionate love involves empathy, understanding, and a genuine desire to help and support others. It often extends beyond personal relationships to include a broader sense of caring for humanity.
Example: Acts of kindness, volunteering, and providing emotional support to those in need are expressions of compassionate love. For instance, someone might volunteer at a shelter or support a friend through a difficult time.
Anecdote: A friend of mine volunteers at a local food bank and finds that the act of helping others brings them immense joy and fulfillment. They describe their compassionate love as a way to connect with and support their community.
Question: How does compassionate love influence your interactions with others? Reflecting on this can help you understand the impact of empathy and kindness in your life.
Statistic: Research from The Greater Good Science Center shows that individuals who engage in acts of compassion experience increased feelings of happiness and life satisfaction.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the various types of love helps us appreciate the different ways this powerful emotion can manifest in our lives. From romantic love and platonic friendships to familial bonds, self-love, and compassionate care, each form of love contributes uniquely to our overall well-being and fulfillment. By exploring these types of love, reflecting on personal experiences, and recognizing the significance of each form, we can deepen our connections with others and ourselves.
Embracing the diverse expressions of love enriches our lives and fosters a greater understanding of the profound ways in which we relate to one another.
The sources for the information provided in the Article:
Types of Love: What Love Means to Different People
1. Romantic Love: The Classic Narrative
Psychology Today article on romantic love and first impressions:
Read more here
2. Platonic Love: Deep Bonds Without Romance
The Journal of Social Psychology on platonic love and friendships:
Read more here
3. Familial Love: The Bonds of Kinship
Family Relations study on familial love and emotional support:
Read more here
4. Self-Love: Embracing Your Own Worth
Psychology Today research on self-love and well-being:
Read more here
5. Unconditional Love: Loving Without Conditions
The Journal of Emotional Health on the nature of unconditional love:
Read more here
6. Compassionate Love: Empathy and Understanding
The Greater Good Science Center research on compassion and happiness:
Read more here
These sources provide additional insights and research related to the various types of love discussed in the article. They offer further reading and context to deepen your understanding of this complex and multifaceted emotion.